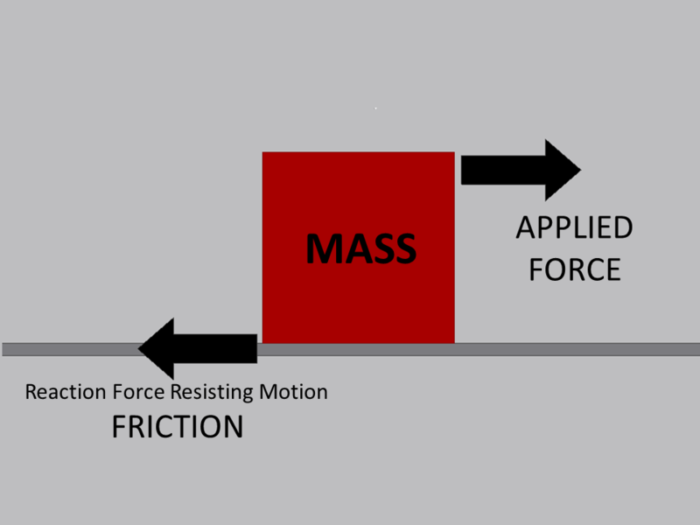
What Friction?
Friction force
- The external force that opposes relative motion between 2 surfaces in contact.
- Friction acts on the surface of contact of both the bodies.
Relative motion
When one object moves relative to another it is called a relative motion.
Why Friction?
Cause of friction
- Friction occurs due to surface irregularities of the two objects in contact.
- Adhesive forces between surfaces in contact.
- Plowing effect.
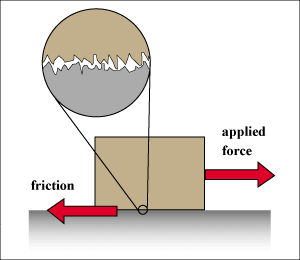
Surface irregularities
- All surfaces when zoomed into a microscopic level contain hills and valleys that interlock when they move or rub on top of each other.
- This unevenness of the surface is called as surface irregularities or roughness.
- Rough surfaces have larger irregularities while smoother surfaces have lesser irregularities.
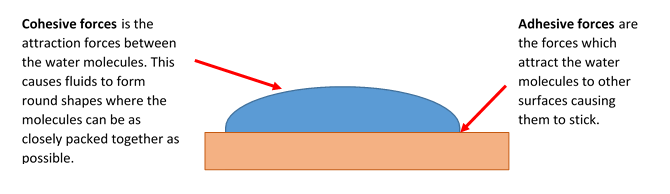
Adhesive forces
- When two surfaces are in contact they start to form bonds and begin to stick to each other. This phenomenon is called as Adhesion.
- When we try to move objects that are on top of another, we are basically breaking the bonds or overcoming the adhesive forces.
Plowing effect
- When surfaces are soft or can change their shape easily, they get deformed when they come in contact with another object. Ex: carpets, when a heavy object is placed on them, it looks like a valley that is caused by the deformation of the shape.
- This effect of the surfaces sinking into each other is known as Plowing effect.
Factors Affecting Friction
Factors affecting friction
Depends on the nature of surfaces in contact. (Friction exists between two surfaces) E.g.: glass and rubber
Nature of surface in contact
- Friction depends on how hard the two surfaces pressed together, as more surface in contact and more bonds are formed→ more bonds to break → means more friction.
- Only the normal reaction force (exactly perpendicular ) to the two surfaces increases friction.
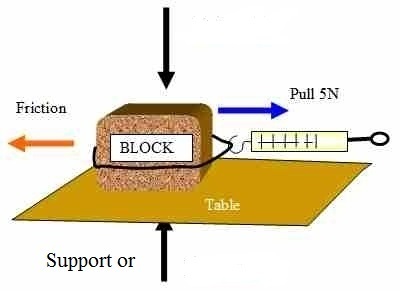
Calculating frictional force using a spring balance
- Using a spring balance we can find the frictional forces opposed by different materials.
- Sandpaper gives a higher reading as compared to stainless steel.
Polishing surfaces in contact to change friction
- Polishing surface reduces irregularities and therefore makes the surface smooth.
- Reduces friction.
Normal reaction force
- Force applied that is exactly perpendicular to the surfaces in contact is called normal reaction force.
- It increases the frictional force.
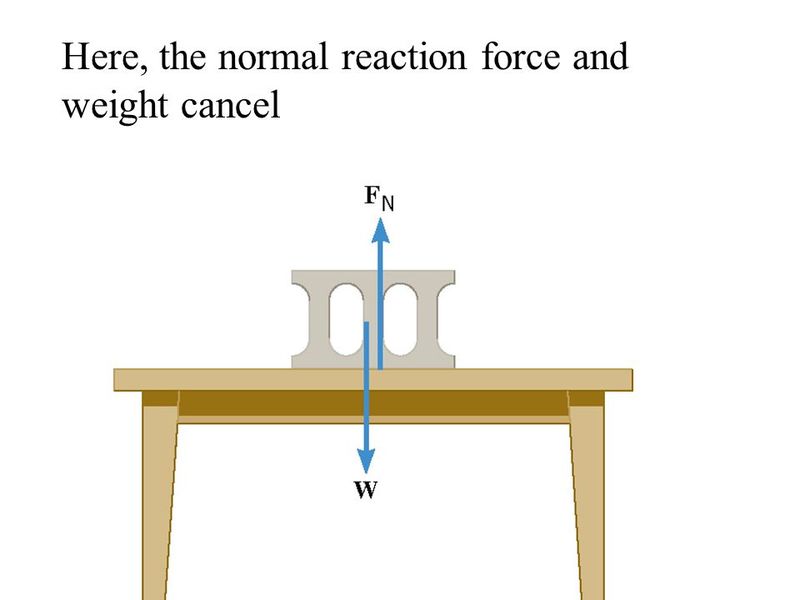
Static Friction
Friction due to a body at rest with the surface in contact is called as Static friction.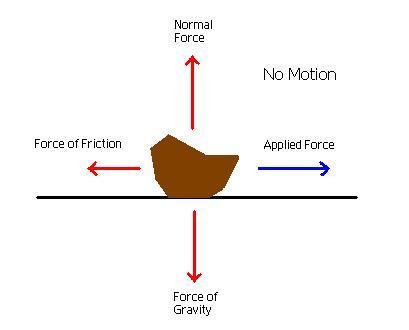
Kinetic Friction
- The friction that comes into play when objects are in motion is called as kinetic friction.
- Kinetic friction:
* Sliding
* Rolling friction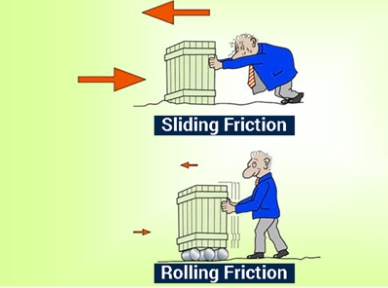
Friction a Frenemy?
How does friction produce heat?
As friction involves breaking bonds, they make the particles vibrate → increase kinetic energy and therefore increase heat.
Applications of friction
Writing, walking, running, tyres on a car, a nail stays in the wall due to friction, usage of a matchstick.
Reinvent the Wheel
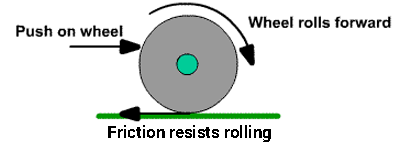
Rolling and using treads to change friction
- Using ball bearings reduces friction as rolling friction is< other types of friction.
- Treads on tyres help expunge water and give better grip, by increasing friction.
Rolling friction
- Rolling provides less friction as compared to sliding.
- Rolling friction < Sliding friction.
- Machines use ball bearings to reduce the friction of moving parts.
Skydiving Cat
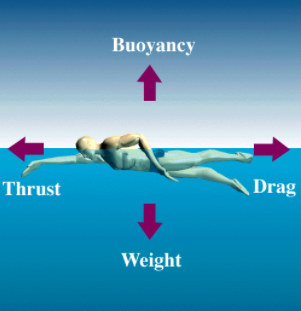
Drag force
- Frictional force exerted by fluids is called drag.
- The drag force on an object depends on speed as well as the shape of the body and nature of the fluid.
Hope you like our work :)
For more chapters you can follow the link given below
For Link



Hello,
May I help you ?